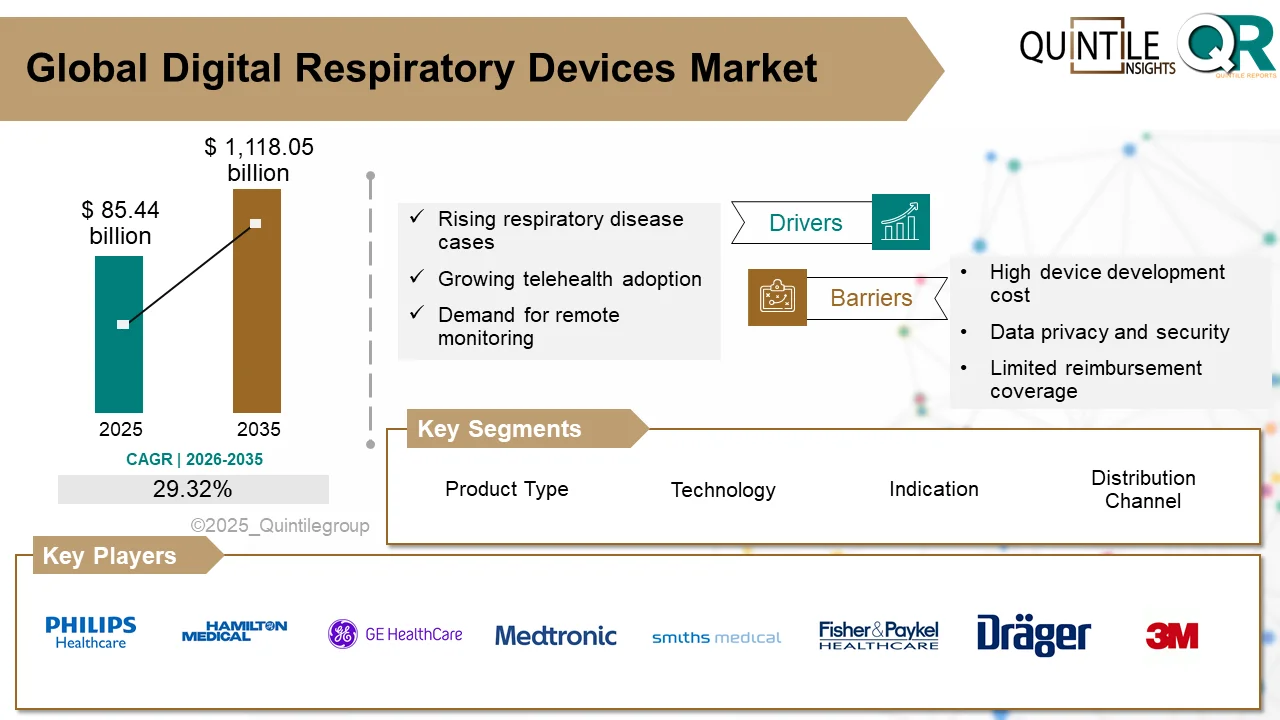
The global Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Testing Market is poised for significant expansion over the next decade, reflecting the growing role of precision diagnostics in modern oncology. According to Quintile Research, the market was valued at USD 2.77 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 7.74 billion by 2035, registering a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035.
Minimal residual disease refers to the small number of cancer cells that remain in a patient’s body after treatment, even when clinical remission is achieved through conventional diagnostic methods. Although often undetectable using traditional imaging or laboratory techniques, these residual cells can lead to disease relapse. As a result, MRD testing has emerged as a critical tool in monitoring treatment response, predicting recurrence, and guiding therapeutic decisions—particularly in hematological malignancies such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Increasingly, MRD applications are also being explored in solid tumors.
The market’s growth is largely driven by the rising global burden of cancer and the increasing risk of relapse associated with blood cancers. As oncology shifts toward personalized treatment approaches, clinicians are relying on highly sensitive MRD assays to tailor therapies according to a patient’s molecular response. This precision-based approach improves outcomes while minimizing unnecessary treatment exposure.
Technological innovation continues to be a major catalyst for market expansion. Advanced platforms such as Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), digital Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and multi-parameter flow cytometry have dramatically improved detection sensitivity and analytical accuracy. These tools enable clinicians to identify cancer cells at extremely low concentrations, enhancing early relapse detection and supporting better-informed treatment strategies. Moreover, MRD is increasingly being used as a surrogate endpoint in clinical trials, accelerating drug development and regulatory approvals.
Supportive regulatory frameworks and expanding reimbursement coverage—particularly in North America—are further strengthening adoption. Medicare approvals for specific MRD assays have improved accessibility and commercial viability. Strategic collaborations between diagnostic developers, biotechnology firms, and academic institutions are also advancing clinical validation and expanding test applications.
Despite strong growth prospects, the MRD testing market faces several challenges. High testing costs, especially for ultra-deep NGS-based assays, can limit accessibility in cost-sensitive healthcare systems. In addition, reimbursement policies remain inconsistent across regions, with some payers categorizing MRD testing as investigational. Technical complexity, infrastructure requirements, and the need for specialized expertise present additional barriers, particularly in emerging markets. Furthermore, the lack of standardized protocols and harmonized reporting frameworks continues to affect cross-study comparability and broader clinical integration.
Regionally, North America leads the global MRD testing market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong regulatory support, and early adoption of precision oncology. Europe follows closely, with Germany, the United Kingdom, and France driving demand through genomic profiling initiatives and value-based care models. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, supported by rising cancer incidence, expanding healthcare investments, and government-led precision medicine programs in countries such as China, Japan, and India.
The competitive landscape is marked by rapid innovation and strategic expansion. Key players operating in the market include Guardant Health, Natera Inc., Adaptive Biotechnologies, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Illumina Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Quest Diagnostics, LabCorp, Qiagen N.V., and others. Companies are focusing on improving assay sensitivity, reducing turnaround times, and expanding into liquid biopsy-based MRD solutions. Recent mergers, acquisitions, and Medicare coverage approvals have intensified competition, particularly in the circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) segment.
Looking ahead to 2035, the MRD testing market is expected to remain a cornerstone of precision oncology. Continued investments in genomic research, expanding clinical utility across tumor types, and integration into routine cancer care pathways will sustain long-term growth. As healthcare systems increasingly prioritize early detection and personalized therapy, MRD testing is positioned to become an essential component of global cancer management strategies.
1. What is Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) testing?
Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) testing is a highly sensitive diagnostic method used to detect very small numbers of cancer cells that remain in a patient’s body after treatment. These cells are often undetectable through conventional imaging or laboratory techniques but may lead to relapse if not identified early. MRD testing is widely used in hematologic cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
2. What is the projected size of the MRD testing market by 2035?
According to Quintile Research, the global MRD testing market was valued at USD 2.77 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 7.74 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 10.8% from 2026 to 2035.
3. What factors are driving growth in the MRD testing market?
Key growth drivers include:
-
Rising global cancer prevalence, particularly blood cancers
-
Increasing demand for precision and personalized oncology treatments
-
Technological advancements in NGS, digital PCR, and flow cytometry
-
Expanding use of MRD as a clinical trial endpoint
-
Supportive regulatory approvals and reimbursement coverage in major markets
4. Which technologies are most commonly used in MRD testing?
MRD testing primarily relies on:
-
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) – Highly sensitive DNA-based detection
-
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – Detects specific genetic mutations
-
Flow Cytometry – Identifies abnormal cancer cells using cell surface markers
-
Digital PCR – Enables ultra-precise quantification of residual cancer DNA
NGS-based and ctDNA (liquid biopsy) approaches are gaining strong momentum.
5. What challenges does the MRD testing market face?
Major challenges include:
-
High testing costs, especially for deep sequencing assays
-
Inconsistent reimbursement policies in some regions
-
Technical complexity and infrastructure requirements
-
Lack of standardized global testing protocols
-
Biological limitations in detecting MRD in solid tumors
6. Which region dominates the MRD testing market?
North America currently leads the global MRD testing market due to strong healthcare infrastructure, FDA approvals, Medicare coverage, and the presence of major biotech companies. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth due to rising cancer incidence and expanding precision medicine initiatives.
7. Who are the key players in the MRD testing market?
Major companies operating in the MRD testing market include:
-
Guardant Health
-
Natera Inc.
-
Adaptive Biotechnologies
-
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
-
Bio-Rad Laboratories
-
Thermo Fisher Scientific
-
Illumina Inc.
-
Quest Diagnostics
-
LabCorp
-
Qiagen N.V.
These companies are focusing on innovation, liquid biopsy expansion, and strategic partnerships.
8. Why is MRD testing important in precision oncology?
MRD testing allows oncologists to:
-
Assess treatment effectiveness
-
Predict relapse earlier than imaging methods
-
Personalize therapy intensity
-
Monitor disease progression in real time
-
Improve long-term survival outcomes
It is increasingly becoming a standard tool in evidence-based cancer management.
Adarsh
Business Strategy — Quintile Reports
Adarsh is a Business Strategy professional focused on transforming market insights into actionable growth plans. He supports strategic initiatives through market analysis, competitive intelligence, and data-driven decision-making to help drive long-term business success.
His core skills include strategic planning, market research, growth opportunity assessment, trend analysis, performance tracking, stakeholder communication, cross-functional collaboration, and critical problem-solving.